Step-by-Step Guide to Applying for the US Food Stamps Program

The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), also known as US Food Stamps Program, stands as one of the United States’ most significant initiatives in addressing food insecurity.
Administered by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), SNAP provides eligible low-income households with financial assistance to purchase food.
Over the years, this program has evolved into a cornerstone of the nation’s efforts to reduce hunger and improve nutritional standards among vulnerable populations.
Learn more about it below and find out how to participate to receive assistance!
Understanding the Purpose of US Food Stamps Program
SNAP’s primary goal is to alleviate food insecurity and ensure that families have access to nutritious meals. Food insecurity—the lack of consistent access to sufficient food for an active, healthy life—affects millions of Americans annually.
By providing financial resources to purchase groceries, SNAP not only combats hunger but also promotes health and well-being.
Key Objectives of SNAP:
- Reducing Hunger: By subsidizing food costs, US Food Stamps Program ensures that families can meet their basic nutritional needs.
- Improving Nutrition: The program encourages healthier eating habits by allowing beneficiaries to buy fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and other essential food items.
- Boosting Economic Stability: SNAP helps low-income families allocate their limited resources more effectively, reducing financial strain.
How to apply for the US Food Stamps Program? Follow these steps
To receive SNAP benefits, you must register and follow certain requirements. Check out the step-by-step guide and information below!
Verify Eligibility
Before starting your application, ensure you meet the program’s eligibility requirements. Eligibility is determined by factors such as household income, size, and certain expenses.
- Check Income Limits: Gross income must typically be at or below 130% of the federal poverty level (FPL). Net income, calculated after deductions like housing and childcare expenses, must also fall below the FPL.
- Assess Household Size: The income threshold varies depending on the number of people in your household. Larger families have higher limits.
- Review Asset Limits: Some states consider savings and investments, though retirement accounts and your primary home are usually excluded.
- Confirm Residency and Citizenship: Applicants must be U.S. citizens or legal non-citizens and reside in the state where they’re applying.
- Understand Work Requirements: Able-bodied adults without dependents (ABAWDs) must typically work or participate in a work program for at least 20 hours a week.
Gather Necessary Documentation
To simplify the application process, collect all required documents beforehand. These may include:
- Proof of Identity: Government-issued photo ID, Social Security card, or birth certificate.
- Proof of Income: Pay stubs, tax returns, or a letter from your employer.
- Expense Documentation: Receipts or bills for housing, utilities, childcare, and medical expenses.
- Residency Proof: Lease agreements, utility bills, or a letter from a landlord
Locate Your State’s SNAP Office
SNAP is administered at the state level, so it’s crucial to find your local office. You can:
- Visit the USDA’s official SNAP website to locate your state’s contact information.
- Call the national SNAP hotline at 1-800-221-5689 for assistance.
Complete the Application
Most states offer multiple ways to apply:
- Online: Visit your state’s official SNAP website to fill out the application electronically. This method is often the quickest.
- In-Person: Visit your local SNAP office to obtain and submit a paper application.
- By Mail or Fax: Download the application form from your state’s SNAP website, fill it out, and send it via mail or fax.
As we said, the registration process must be carried out by the administration of your state. Therefore, there may be differences in the process and registration options.
So, be sure to first check how it works in your state and what will be required of you!
Attend an Interview
After submitting your application, you’ll be contacted to schedule an interview. This step is required to verify your information and discuss your circumstances.
Interviews are typically conducted over the phone or in person at your local SNAP office.
So, be prepared to answer questions about your household, income, and expenses. Provide any additional documents requested.
Wait for Approval
Once your application and interview are complete, your state’s SNAP office will review your case. This process may take up to 30 days.
Expedited services may be available for individuals or families facing extreme financial hardship.
- Approval Notification: If approved, you’ll receive an Electronic Benefits Transfer (EBT) card, which works like a debit card.
- Denial Notification: If denied, you’ll receive a letter explaining the reasons and instructions for appealing the decision.
Tips for a Smooth Application Process
- Double-check your application for accuracy before submission.
- Respond promptly to requests for additional information.
Keep copies of all submitted documents.
Start Using Your Benefits
With your EBT card in hand, you can purchase eligible food items at participating retailers. Remember:
- Benefits are loaded monthly.
- SNAP cannot be used for non-food items, alcohol, tobacco, or hot/prepared foods.
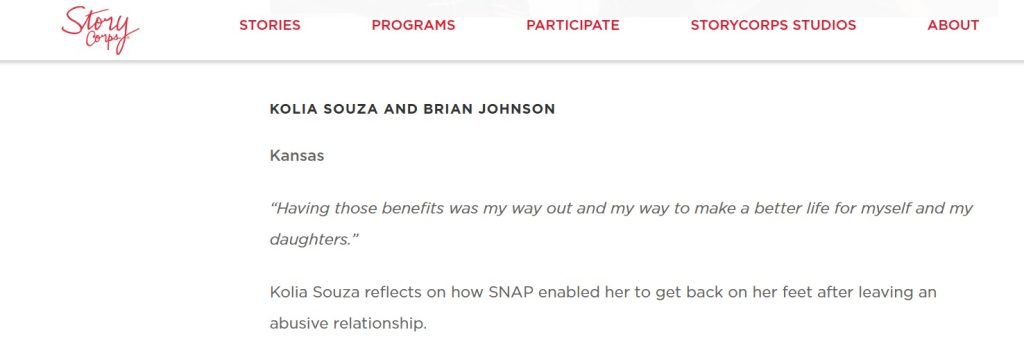
User testimonial about SNAP on the StoryCorps website.
You can also check out a series of user testimonials about SNAP in StoryCorps’ “SNAP Matters: Stories Recorded with Support from the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation.”
Challenges and Criticisms of SNAP
While US Food Stamps Program has undeniably positive impacts, it also faces challenges and criticisms.
Addressing these concerns is vital to enhancing the program’s effectiveness and ensuring its long-term sustainability.
1. Stigma and Misconceptions
Many recipients face stigma associated with using government assistance programs.
Public education efforts are essential to dispel myths and promote understanding of SNAP’s role in supporting communities.
2. Benefit Adequacy
Some critics argue that SNAP benefits are insufficient to meet the nutritional needs of families, particularly in areas with high food costs.
Advocates call for adjustments to benefit levels to reflect regional cost variations.
3. Fraud and Misuse
Although the incidence of fraud in SNAP is low, instances of misuse can undermine public trust.
Strengthening oversight and implementing stricter controls can address this issue.
4. Accessibility
Navigating the application process can be challenging for some individuals, particularly those without internet access or familiarity with digital platforms.
Simplifying application procedures and offering assistance can increase program participation.
Innovations and Future Directions
To maximize its impact, SNAP continues to evolve, incorporating new technologies and strategies to better serve recipients and address emerging challenges.
1. Modernizing Technology
The adoption of electronic benefit transfer (EBT) cards has streamlined the distribution of SNAP benefits, making transactions more secure and convenient.
Further technological advancements, such as mobile apps for benefit management, can enhance user experiences.
2. Expanding Access to Healthy Foods
Programs like Double Up Food Bucks incentivize SNAP recipients to purchase fresh produce by matching their spending at farmers’ markets.
These initiatives promote healthier eating while supporting local agriculture.
3. Addressing Food Deserts
In areas with limited access to grocery stores, partnerships with online retailers and community organizations can improve food availability.
Expanding SNAP’s acceptance at delivery services and food pantries is another promising solution.
4. Strengthening Nutrition Education
Programs such as SNAP-Ed provide recipients with information on meal planning, budgeting, and healthy cooking. By empowering families with knowledge, these initiatives help maximize the nutritional impact of SNAP benefits.
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) is far more than a food assistance initiative; it is a lifeline for millions of Americans and a catalyst for economic and social progress.
By addressing food insecurity, promoting healthier lifestyles, and stimulating local economies, SNAP plays a critical role in building stronger, more resilient communities.
While challenges remain, ongoing innovations and a commitment to improvement ensure that SNAP will continue to adapt and meet the needs of future generations.
Understanding and appreciating the broader impact of SNAP is essential for fostering support for this invaluable program, which not only feeds the hungry but also nourishes the nation as a whole.
Start exploring everything about SNAP by visiting the official website!